Su Shi once described the beautiful scenery of the south of the Yangtze River in "Drinking Lake". "The water is bright and sunny, and the mountains are empty and rainy. If you want to make West Lake better than Xizi, light makeup is always suitable". Time flies, the three-autumn osmanthus, ten-mile lotus, the smoky willow painting bridge and the beauty of the West Lake continue, relying on our care for the ecology of the earth home. As the population grows, the earth's resources are becoming increasingly scarce, which brings more and more severe survival challenges to mankind; and the non-renewable fossil energy sources force us to vigorously develop clean renewable energy. The efficient use of renewable energy depends on the development of energy storage technology. The water-based organic flow battery that uses water as the medium is an energy storage system with high safety.
Recently, Wang Pan's research group at the Faculty of Science of West Lake University and its cooperation team developed a new biomimetic design of water-soluble phenazine compounds, which endows the aqueous organic flow battery system with excellent stability (ie, extremely low battery capacity degradation). This research provides a new high-stability water-based organic molecular structure framework design strategy, and provides an important theoretical basis for the further design and construction of high-performance water-based flow batteries. Recently, this achievement was published as a cover article in the top chemistry journal "Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.". Pang Shuai, a 2020 doctoral student in Wang Pan's research group, is the first author, and research assistant Wang Xinyi is the second author.

1 Flow battery trend: water-based organic flow battery
In recent years, the rapid development of energy storage technology has greatly improved the utilization rate of renewable energy, which has led to a rapid reduction in the cost of renewable energy power generation systems represented by wind power and photovoltaics, which is effective in reducing the use of fossil energy and reducing carbon emissions. way. However, because renewable energy is affected by the earth's rotation and changes in wind, rain, and snow, there are intermittent volatility (ie intermittent supply), which puts forward higher requirements for safety, stability, and reliability of large-scale energy storage regulation systems .
The flow battery can convert electrical energy into chemical energy for storage. It stores and releases energy through the redox reaction of active materials on the electrode surface. The capacity for storing electric energy is determined by the size of the external storage tank, so that the energy conversion of the battery does not depend on the size of the electrode, but the total amount of electrolyte.
As a kind of flow battery, the water-based organic flow battery uses water as a medium and is an energy storage system with high safety. Its active materials are derived from elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen, which are abundant in nature. These elements are editable and adjustable in molecular structure, and can complete the mutual conversion of chemical energy and electrical energy through the redox behavior of organic functional groups. . The multi-electron transfer in organic molecules and its diverse designability endow the water-based organic flow battery with unique and flexible advantages, making it a new trend in the development of flow batteries.
2 Can amino acids in nature bring "new hope"?
In the field of water-based flow batteries, a series of molecules based on organic structural frameworks such as anthraquinone, viologen, ferrocene, aza aromatic ring, etc., have shown relatively good performance and application prospects. However, most of the current research work is based on commercially available known functional dye molecules; derivatives based on the phenazine organic structure skeleton, there are only a few examples reported in the previous report, all of which have poor water solubility and chemical reactions. Decomposition (ie instability) and other issues, and the attenuation mechanism of such compounds is not clear.
In order to improve the status quo, researchers at West Lake University set their sights on amino acids that are widely sourced in nature. As the basic unit of protein, amino acid is the basic material for normal metabolism and life-sustaining. Through folding and assembly, the specific molecular structure of protein is formed, giving it biological activity. Researchers innovatively used amino acids as functionalized groups (ie functional groups), introduced into the phenazine skeleton, and synthesized a series of different substituent functions at different positions through a simple one-step coupling reaction, taking advantage of the water solubility and electron donating properties of amino acids Chemical, water-soluble phenazine derivatives (AFP) with two electron transfer centers.
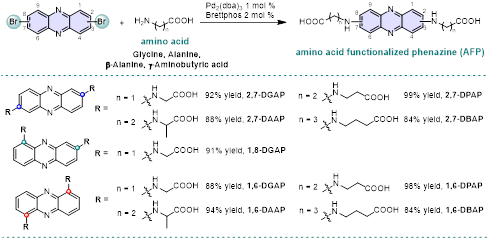
Figure 1 Synthesis of amino acid functionalized phenazine derivatives (AFP)
3 1,6-AFP: Create an aqueous flow battery with an annual attenuation of only 0.5%
The electron donating properties of amino acids reduce the redox potential of the battery and broaden the operating voltage range of the flow battery; the natural water-soluble characteristics of amino acids further increase the energy density of the flow battery.
The research group systematically explored the effects of different "members" of the "AFP family" of phenazine derivatives (ie, different branches and different positions of amino acids) on the performance of water-based flow batteries. Combined with analytical methods such as nuclear magnetism, high-resolution mass spectrometry, and CV testing, they investigated the stability of these compounds in the oxidation/reduction state.

Figure 2 "Simplified" water flow battery system
Studies have shown that 1,6-AFP has stable oxidation and reduction states; although 1,8-AFP and 2,7-AFP also have stable oxidation states, their reduced states are prone to hydrogen tautomerism and loss The redox activity is further degraded, and its capacity rapidly decays in the battery test. The researchers used density functional theory (DFT) calculations, combined with experimental results, to make a detailed analysis of the attenuation mechanism of these compounds, and at the same time made a systematic summary and prediction of other different amino acids and substitution positions.
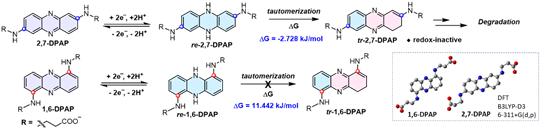
Figure 3 Degradation pathway and mechanism of AFP
The star molecule 1,6-AFP performs well in the long-term constant pressure charge-discharge cycle of water-based flow batteries at pH 8,1M electron concentration. After 99 days of experimental testing, no chemical decomposition was observed by nuclear magnetic and electrochemical means. The flow battery has extremely low capacity attenuation (0.000002% per circle, 0.0015% per day), and under long-term charging and discharging, it only shows an attenuation of 0.5% per year-this is the current report, the organic flow The new record holder of low battery attenuation has strong application value in water-based energy storage systems.
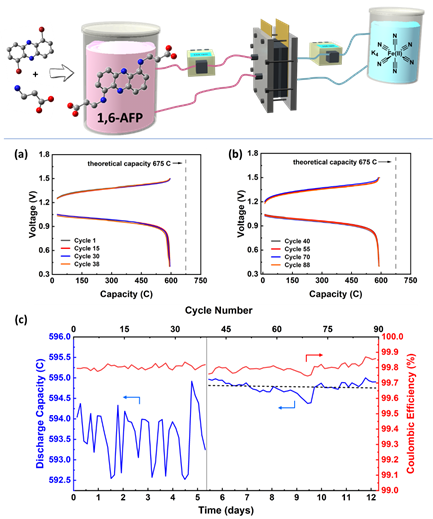
Figure 4 1 M 1,6-AFP (pH 8) battery cycle performance
4Organic polymer materials laboratory: aiming at "new materials"
This research is the first achievement of the organic polymer materials laboratory led by Wang Pan, a distinguished researcher of the School of Science of West Lake University.
In fact, at West Lake University, Wang Pan is leading the team to "break" into a field that is also very new to her. Before joining the Faculty of Science of West Lake University in November 2019 and becoming a doctoral supervisor, Wang Pan was mainly engaged in metal organic chemistry research, that is, the use of metal organic catalysts to study the synthesis of chiral compounds, for the development of new drugs and new materials-in Massachusetts During the postdoctoral period in the Polytechnic Institute, Wang Pan came into contact with more new organic materials with different structures and functions. This work also "opened the horizon" for current scientific research.

Figure 5. Researcher Wang Pan (first from right in the second row) leads the team to explore new materials
Now, as the "helm" of the laboratory, Wang Pan, based on his own experience, leads everyone to the new direction of "interdisciplinary": "The development of new materials with synthetic chemistry as a tool is the main research direction of the laboratory. "At present, this laboratory is working in the cross-fields of organic synthetic chemistry, energy chemistry, and materials chemistry, designing and developing new materials, and modifying the structure of organic materials and adjusting their physical and chemical properties at the molecular level.
In the topic of the new biomimetic design of water-soluble phenazine compounds synthesized this time, although the research coincides with the general background of the new crown epidemic, it has encountered problems such as the difficulty of transporting experimental equipment and equipment parts from overseas. The team is still only A breakthrough was made in half a year. The first author, the first doctoral student in the laboratory, and Pang Shuai, a new 2020 doctoral student who joined West Lake University, recalled that he encountered difficulties in material synthesis, product instability, and construction of test equipment. Pang Shuai, who specializes in organic chemistry, is also the first time he came into contact with the electrochemical field. At this time, the guidance of his instructor gave him great help: "Including the work of chemical synthesis, battery equipment design, and testing. The teacher’s guidance is definitely not possible."
Shower Set,Lift Rod Shower Set,Shower Set With Faucet,Thermostatic Shower Set
AIHUI Sanitary Ware , https://www.fsaihuisanitary.com