Third, the final heat treatment
After the above forging, small mold finishing, and medium and large mold roughing, in order to impart final mechanical properties to the mold, quenching and high temperature tempering are required to obtain the desired structure of the matrix structure to ensure high strength and toughness.
Due to the good hardenability of hot forging die steel, oil cooling can be used. At the same time, in the process of mold making, according to the structure of the die, the structure and material of the die forging, the hardness and toughness required by the die, etc. Requirements, choose the conventional quenching heat treatment, austempering heat treatment and high temperature quenching heat treatment three methods, that is, using 840 ~ 860 °C quenching or 900 °C high temperature quenching and different cooling methods, using the same tempering process to obtain different strong Plastic fit to increase the life of the mold.
Conventional quenching heat treatment process
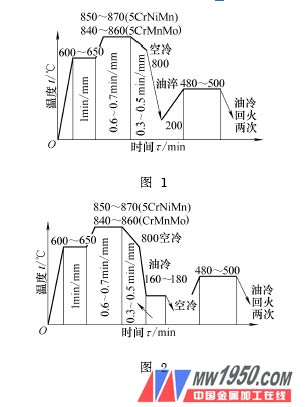
In the past, after the mold was pre-annealed, in order to give the final mechanical properties of the mold and the mold to achieve the required performance, the heat treatment shown in Figure 1 was often used. In order to reduce internal stress and deformation, the forging die is taken out from the furnace and pre-cooled to 800 °C in air, then oil quenched, quenched and cooled at about 200 °C in time to temper. The purpose of tempering is to retain more retained austenite and avoid quenching and cracking. However, due to the large heat storage energy of the hot forging die, when the surface temperature is cold to about 200 °C, the core temperature is still high, so the heart is A large amount of retained austenite will transform into pearlite or coarse upper bainite structure during tempering. The upper bainite structure is a structure in which discontinuous carbides are distributed between ferrite sheets, and the crack propagation resistance is small. This kind of structure is difficult to maximize the potential of material toughness, and the service life of the mold is low, often in use. An early break occurred.
2. Austempering heat treatment process
After forging, annealing, roughing and finishing, the forging die is subjected to austempering and tempering according to Fig. 2, so that the matrix structure obtains the pleated martensite lower bainite multiphase structure, which can fully exert the lower bainite. Advantage. The lower bainite structure is distributed with fine and fine carbides in the supersaturated ferrite, and the crack propagation resistance is large and the lath-like (dislocation type) martensite phase is similar, and the plasticity is high in the case of good plasticity. Therefore, in the case of substantially the same hardness, the impact toughness is remarkably improved, and the wear resistance of the mold is insufficient, but the contour induction hardening method can be performed by using a portion with a strong working cavity to improve the service life of the mold.
3. High temperature quenching heat treatment process
In order to further improve the life of the mold and increase the quenching temperature of the mold, the conventional heat treatment process is adjusted, and the quenching temperature is increased to 900 °C under the conditions of other process parameters (see Fig. 3), and the service life of the mold is improved. 2. 5 times. Although the quenching temperature is increased, the austenite grains are significantly coarsened, but the fracture toughness is increased by 70% to 125%. This is mainly because the overheating quenching improves the fracture toughness of the mold. The mechanism of change mainly has the following aspects:
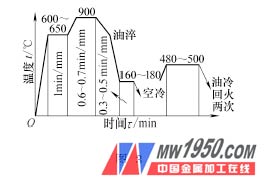
(1) The amount of retained austenite is increased, and the sheet of retained austenite is surrounded by the martensite sheet. The crack stops when it passes through the martensite and is transferred to the retained austenite, so the thin layered austenite has an effect of inhibiting crack propagation.
(2) 5CrNi Mo and 5CrMnMo generate a large amount of twin martensite (sheet martensite) during ordinary heating, and more lath (dislocation type) martensite can be produced during overheat quenching. The lath martensite has high strength and toughness, and the crack propagation resistance is large to increase the toughness. Therefore, the superheated quenching is often used for heat treatment requiring strengthening and toughening to improve the service life of the mold.
(3) Carbides and inclusions can dissolve into austenite, reducing the core of micropores.
Fourth, the conclusion
The service life of hot forging die is closely related to the mold design, materials and process methods. Therefore, in the process of mold making, reasonable selection of materials should be carried out according to the conditions of the mold and the required mechanical properties, and the process should be carried out. Control, especially heat treatment process control is particularly important, only a reasonable heat treatment method can meet the high wear resistance of hot forging die, maintain high strength and good impact toughness and thermal ablation at working temperature (including High thermal fatigue resistance, oxidation resistance and heat resistance) and resistance to heat washout.
The hot forging die treated by the above three heat treatment methods has been applied in the company, and the austempering and high temperature quenching heat treatment processes have achieved good results in improving the life of the die, and achieved good economic benefits.
Previous page
Sensor Night Light,Led Strip For Sensor,Motion Sensor Night Light,Auto Sensor Night Light
NINGBO ZHENGUO INTELLINGENT LIGHTING CO.,LTD , https://www.zguolight.com