[ Huaqiang Security Network News ] 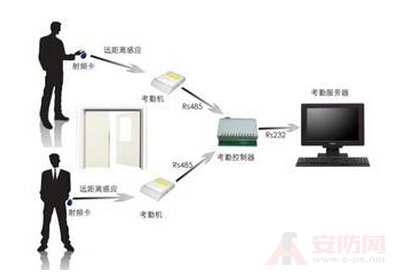
This article focuses on the introduction of the composition and characteristics of radio frequency identification technology.

Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless communication technology that uses radio signals to identify specific targets and read and write related data without the need to identify mechanical or optical contact between the system and a particular target.
The radio's signal is transmitted from the tag attached to the item by an electromagnetic field that is modulated into a radio frequency to automatically identify and track the item. Some tags receive energy from the electromagnetic field emitted by the recognizer when they are recognized, and do not require a battery. The tag itself has a power source and can actively emit radio waves (electromagnetic fields that are modulated into radio frequencies). The tag contains electronically stored information that can be identified within a few meters. Unlike barcodes, RF tags do not need to be within the line of sight of the recognizer, but can also be embedded within the object being tracked.
Radio frequency identification technology is used in many industries. Attaching the label to a car that is in production, the factory can easily track the progress of the car on the production line. The warehouse can track where the medicine is located. RF tags can also be attached to livestock and pets to facilitate positive identification of livestock and pets (positive identification means preventing several animals from using the same identity). The RFID-enabled identification card allows employees to access the locked building section, and the RF transponder on the car can also be used to collect the toll road and parking lot.
Some RF tags are attached to clothing, personal belongings, and even implanted in the human body. Because this technology may read personal information without my permission, this technology may also infringe on personal privacy concerns.
Radio frequency identification technology component
Transponder: consists of an antenna, a coupling element and a chip. Generally, the tag is used as a transponder. Each tag has a unique electronic code attached to the object to identify the target object.
Reader: A device consisting of an antenna, a coupling element, a chip, and reading (and sometimes writing) tag information. It can be designed as a handheld rfid reader or a fixed reader.
Application software system: It is application layer software, which mainly processes the collected data and uses it for people.
    Radio frequency identification technology features
Radio frequency technology
The most important advantage of RFID systems is non-contact identification, which penetrates the harsh environment of snow, fog, ice, paint, dirt and bar codes that are not usable, and is extremely fast to read, in most cases less than 100 milliseconds. The ability to write to an active RFID system is also an important advantage. Can be used for interactive services such as process tracking and maintenance tracking.
The main problem that constrains the development of RFID systems is the incompatibility standard. The major manufacturers of RFID systems provide dedicated systems, resulting in different applications and different industries using different vendors' frequency and protocol standards. This confusion and separatism has restricted the growth of the entire RFID industry. Many European and American organizations are working on this issue and have achieved some results. Standardization will certainly stimulate the substantial development and wide application of radio frequency identification technology.
applicability
The essence of logistics management is to achieve the two purposes of reducing costs and improving service levels through the management of the whole process of logistics. How to get the right products at the right time and in the right place with the right cost and the right conditions has become the highest goal pursued by logistics companies. Generally speaking, the value of enterprise inventory accounts for about 25% of the total assets of the enterprise, accounting for more than 50% of the current assets of the enterprise. Therefore, the core of logistics management is the management of inventory in the supply chain.
The use of radio frequency identification technology in transportation management requires only the installation of electronic tags on the outer packaging of the goods, and the setting of readers at the transport checkpoints or transfer stations to realize the visual management of assets. At the same time, the owner can access the in-transit visualization webpage to understand the specific location of the goods according to the authority, which is of great significance to improve the service level of the logistics enterprise.
Performance characteristics
1. Quick scan. The RFID recognizer can recognize and read several RFID tags at the same time!
2. The size is small and the shape is diverse. RFID is not limited in size and shape on reading, and it does not need to match the fixed size and print quality of the paper for reading accuracy. In addition, RFID tags can be developed into smaller and more diverse forms for use in different products.
3. Anti-pollution ability and durability. Traditional bar code carriers are paper and are therefore susceptible to contamination, but RFID is highly resistant to substances such as water, oil and chemicals. In addition, since the bar code is attached to a plastic bag or an outer carton, it is particularly susceptible to breakage; the RFID tag is to store data in the chip and thus be protected from fouling.
4. Can be reused. Nowadays, barcode printing cannot be changed after it is printed. RFID tags can repeatedly add, modify, and delete data stored in RFID tags to facilitate information update.
5. Penetrating and barrier-free reading. In the case of being covered, RFID can penetrate non-metallic or non-transparent materials such as paper, wood and plastic, and can communicate transparently. The barcode scanner must be able to read the barcode at close range without object blocking.
6. The data has a large memory capacity. The capacity of the one-dimensional barcode is 50 Bytes, the maximum capacity of the two-dimensional barcode can be stored from 2 to 3000 characters, and the maximum capacity of the RFID is MegaBytes. With the development of the memory carrier, the data capacity has also been expanding. The amount of information that will be carried in future items will increase, and the demand for capacity expansion of the volume label will increase accordingly.
7. Security. Since RFID carries electronic information, its data content can be protected by passwords, making its content difficult to be forged and altered.
RFID has attracted attention because of its long-distance reading and high storage capacity. It not only helps a company to significantly improve the efficiency of goods and information management, but also allows sales companies and manufacturing companies to interconnect, so as to more accurately receive feedback, control demand information, and optimize the entire supply chain.
There are variety types of cellulose ether available in the market and HPMC and HEMC are most popular used in construction industry. Cellulose ether can greatly improve the water retention effect for wet mortar, which is adapt to various mortar applications based on viscosity and grade type. Innocel offers various grades of cellulose ether product which is suitable for tile adhesive, plaster, wall putty, EIFS and self-leveling compound etc.
Cellulose Ether,Hpmc Cellulose Ether,Methyl Ether Cellulose,Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose
Shanghai Na Long Tech Co., Ltd , https://www.na-long.com